Pipeline
Transcriptomics drug discovery
Transcriptomics drug discovery is a revolutionary drug discovery approach that identifies the mechanism of action of small molecules through transcriptome analysis, and that addresses genetic disorders and cancer by intervening transcriptome* with small molecules.
transcriptome* : the collection of all RNAs expressed in a cell at a specific time and under certain conditions
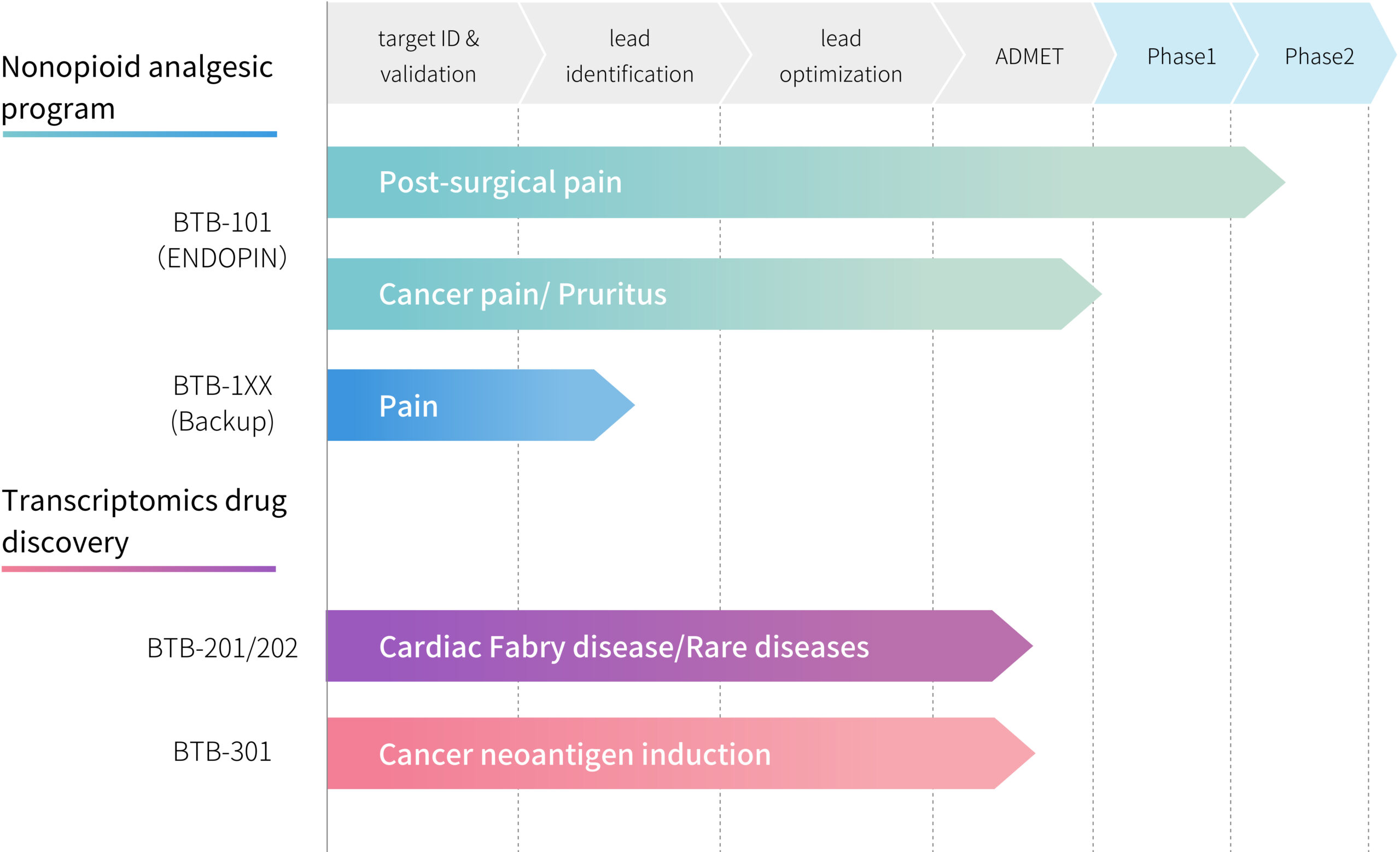
Nonopioid analgesic program
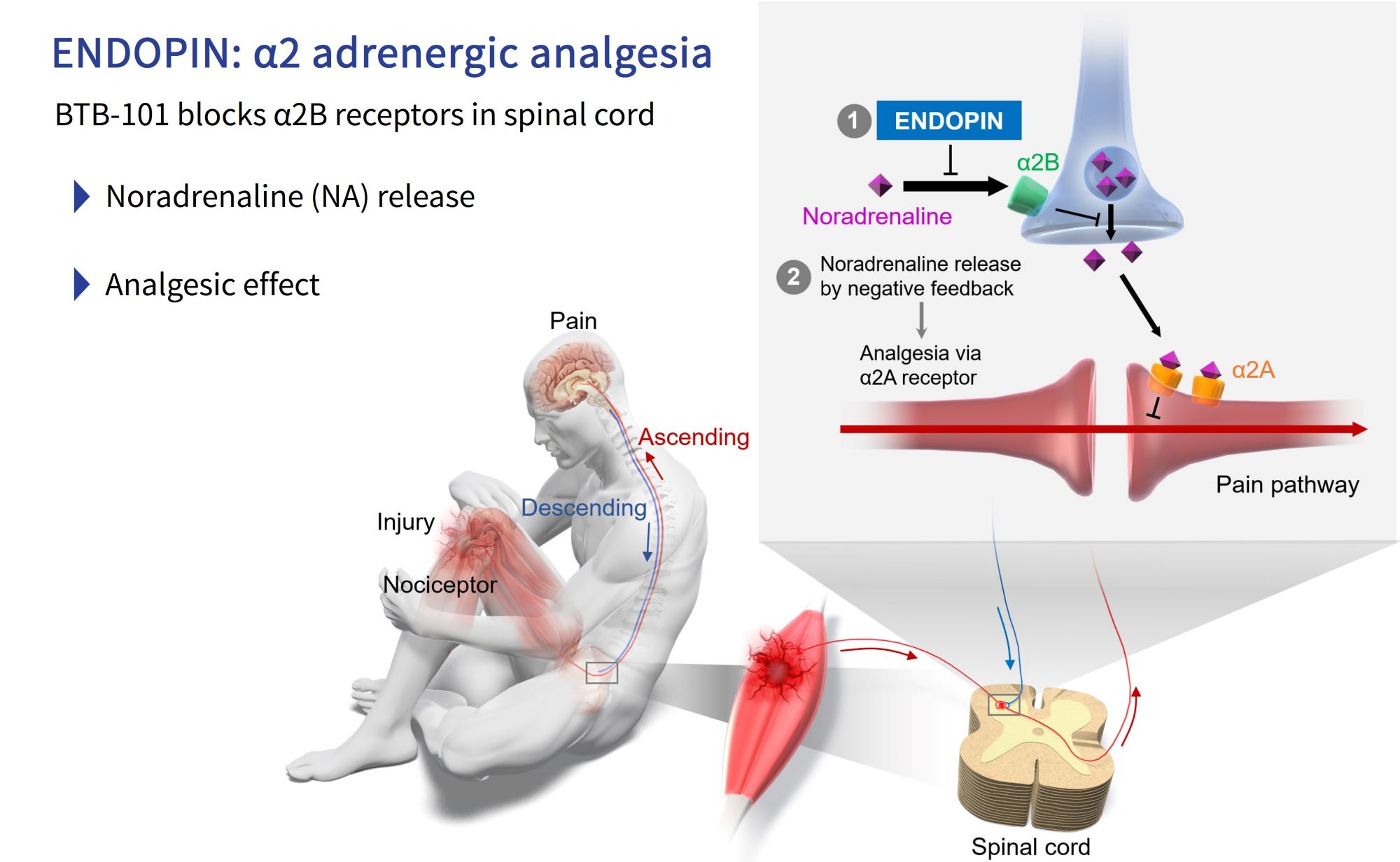
BTB-101 (ENDOPIN): A non-opioid analgesic compound with a novel mechanism of action
BTB-101 is the world’s first small molecule discovered through transcriptome analysis (the collection of RNA expressed from the genome) that inhibits the α2B adrenergic receptor. BTB-101 has the characteristic of having a strong analgesic effect similar to that of opioids in preclinical animal data, but does not show side effects or dependence in the therapeutic range. With the potential to provide a safe and effective treatment option to manage patients’ pain, BTB is developing BTB-101 as a first-line analgesic agent that can help resolve the opioid crisis in the United States and beyond.
RNA regulatory drug development program
Compared with nucleic acid-based medicines, small molecule-based RNA splicing regulators have favorable manufacturing costs and can be administered orally for long periods of time. As a single compound is effective against multiple genetic diseases, demonstrating efficacy for one genetic disease increases the potenital for application for other rare genetic diseases and opens the door for preemptive medicine preventing disease onset for thousands to millions of people affected.
Rare genetic disease program
BTB-201: Target disease: Cardiac Fabry disease
BTB is developing a small molecule drug to treat Cardiac Fabry disease, which is caused by abnormal RNA splicing of the alpha-galactosidase A (GLA) gene and is currently treated with an expensive and only moderately effective enzyme replacement therapy.
BTB-202: Target disease: Long QT syndrome
BTB is developing a treatment that addresses the abnormal RNA splicing of cardiac ion channels, which is the most common cause of the long QT syndrome, a major cause of sudden death in young people.
In addition, this compound induces the splice-neoantigens in cancer cells, demonstrating the enhancements of immune checkpoint inhibitors in preclinical studies.
Enhancements of cancer immunotherapy
BTB-301: Enhancing the expression of cancer-specific spliced neoantigens
BTB-301 is a small molecule that enhances the expression of spliced neoantigens, and the compound has demonstrated the enhancements of immune checkpoint inhibitors in preclinical studies.
